The main difference between Fuji absolute pressure transmitter and gauge pressure transmitter
The concept of pressure type is involved in the selection of pressure transmitters: absolute pressure, gauge pressure, negative pressure and differential pressure.
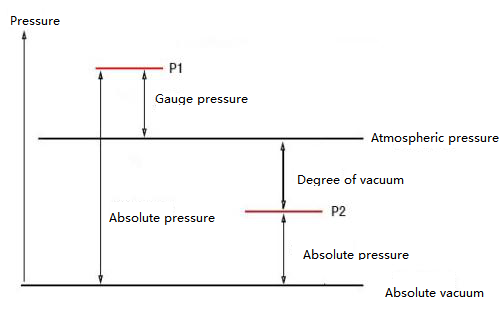
Although their explanations are a bit difficult to understand, the principle is actually very simple. You only need to know this. The principles of these four pressure transmitters are all based on the principle of differential pressure, that is, one side is connected to the medium pressure, and the other side is the reference pressure. The difference is that the pressure connected to the reference pressure side is different.
For example, the absolute pressure transmitter measures the absolute pressure of the medium in the device, and its reference pressure is the absolute value of 0, which has nothing to do with the atmospheric pressure, so there will be a vacuum sealed cavity on the low pressure side of the pressure core.
The gauge pressure transmitter measures the pressure based on atmospheric pressure. One side of the pressure transmitter is connected to the atmosphere, and the other side is connected to the measured pressure, so the reference pressure side is open to the atmosphere. For measuring liquid level in pipes and non-pressure tanks. If you pay close attention to the casing of some pressure transmitters, it is not difficult to find some small holes on it. These ventilation holes are reserved to keep the reference side connected to the atmosphere.
Differential pressure transmitters have two pressure tubes to measure differential pressure. If the differential pressure transmitter is only connected to the positive membrane chamber or the negative membrane chamber, its function is equivalent to a general gauge pressure transmitter. The pressure ports on both sides of the normal differential pressure transmitter will be connected to different pressures respectively. It is common to measure the liquid level of the sealed tank according to the pressure difference, and use the orifice plate to measure the flow of the pipeline.
In addition, the concept of static pressure is often heard, but it is easy to confuse that static pressure is not a pressure type. For example, a pressure transmitter with a maximum static pressure of 25Mpa means that when the pressure on both sides of the pressure transmitter is the same and lower than 25Mpa, the pressure of the pressure transmitter is displayed as 0. However, when the pressure on both sides of the ordinary differential pressure transmitter rises above 25MPa at the same time, the displayed result will be distorted and will no longer be 0. For this reason, high static pressure differential pressure transmitters are mostly used in flow, liquid level measurement and high pressure applications.
